GCSE Standard Questions: Electric Circuits
Q15.
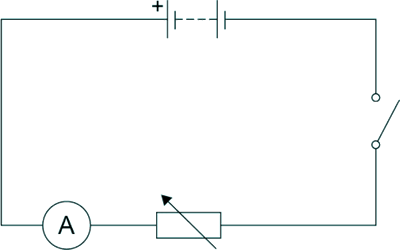
(a) Lex investigated how the current in a series circuit varied with the resistance of a variable resistor. The diagram below shows the circuit he used:
This graph shows his results:
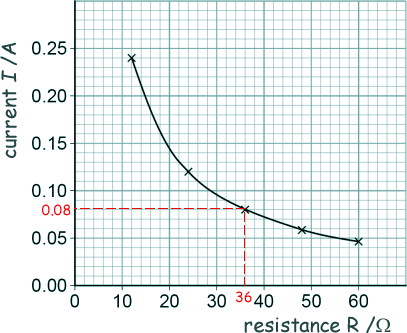
(i) The battery had a power output of 230 mW when the resistance of the variable box resistor was 36 Ω.
Determine the potential difference across the battery.

P = I V
V = IR
I = V/R
P = V2/R 
230 x 10-3  = V2/ 36
= V2/ 36
V2 = 230 x 10-3 x 36 
V2 = 8.28 
V = 2.88 volts 
P = IV
I = 0.08 A - from the graph 
0.230  = 0.08 × V
= 0.08 × V
V = 0.230 /0.08 
V = 2.88 volts 
[4 marks]
(ii) Lex concluded: 'the current in the circuit was inversely proportional to the resistance of the variable resistor.'
Explain how the results on his graph show that he is correct.



[2 marks]
(b) The diagram below shows a circuit with a switch connected incorrectly.
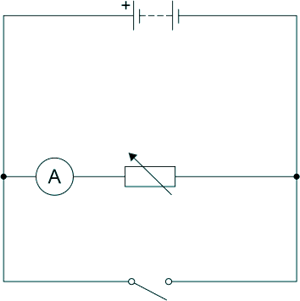
Explain how closing the switch would affect the current in the variable resistor.
When you close the switch you cause a short circuit.  The current would be almost zero in the variable resistor because the switch has effectively zero resistance
The current would be almost zero in the variable resistor because the switch has effectively zero resistance , therefore most of the current would flow through the path with the switch in it not the one with the resistor in it.
, therefore most of the current would flow through the path with the switch in it not the one with the resistor in it. 
[3 marks]
(Total 9 marks)









