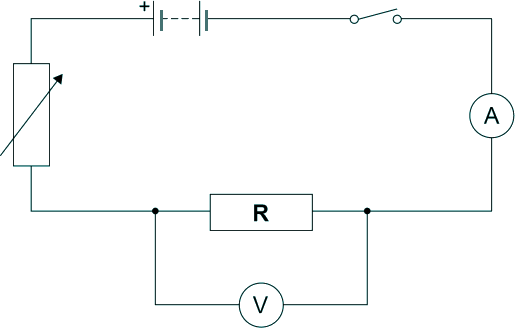
GCSE Standard Questions: Electric Circuits Q14. (a) Chloe investigated how the current in resistor R varied box with the potential difference across the resistor. She maintained a constant temperature for the resistor throughout the experiment. She recorded both positive and negative values of current in her notebook. Here is the circuit Chloe used:
Describe a method that Chloe could have used for this investigation. [6 marks]
It is not just a 'tick fest' - but a marker does look to see how many relevant points you have made, then considers how you have strung them together to put your answer into a 'level'
Indicative content:
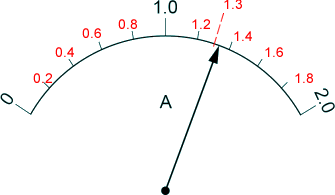
(b) Lois repeated the investigation. During Lois's investigation the temperature of resistor R increased. Explain how the increased temperature of resistor R would have affected Lois's results. The current and p.d. would not be directly proportional when she plotted the graph. Therefore her I-V graph would not be a straight line, it would be curved [2 marks] (c) The diagram shows the scale on the analogue moving coil ammeter Chloe used, at one time in the investigation.
[2 marks] (d) Lois replaced the moving coil ammeter with a digital ammeter. The diagram shows a reading on the digital ammeter.
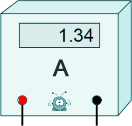
The digital ammeter has a higher resolution than the moving coil ammeter.
[2 marks] (Total 12 marks) |
Follow me...
|