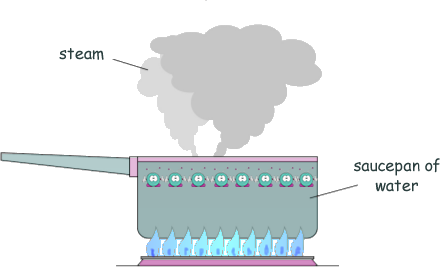
Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Questions - GCSE standard Q8. The diagram shows water being heated. Eventually the water changed into steam.
(a)
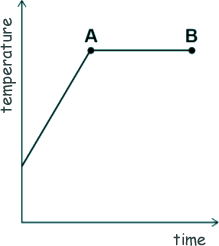
[2 marks] (b) The sketch-graph shows how the temperature of the water varied with time.
What is the name of the process that is taking place between points A and B? Give a reason for your answer. The process is the boiling [2 marks] (c) A mass of 63 g of water was turned into steam. The specific latent heat of vaporisation of water is 2.26 MJ/kg Calculate the thermal energy transferred to the water to turn it into steam. 63g = 0.063 kg ΔQ = ml ΔQ = 0.063 x 2.26 ΔQ = 0.14
[4 marks] (d) The mass of the steam was 0.063 kg. The volume of the steam was 0.105 m3 Calculate the density of steam. Density = mass/volume ρ = m/V ρ = 0.063/0.105 ρ = 0.60
[3 marks] (Total 11 marks) |
Follow me...
|