Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Questions - GCSE standard Q12. Lily heated water in an electric kettle.
Water has a high specific heat capacity. (a) Complete the sentence below by choosing answers from this box.
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg [2 marks] (b) The kettle circuit contains a thermistor which is used to switch the kettle off when the water reaches 100 °C. Draw the correct symbol for a thermistor.
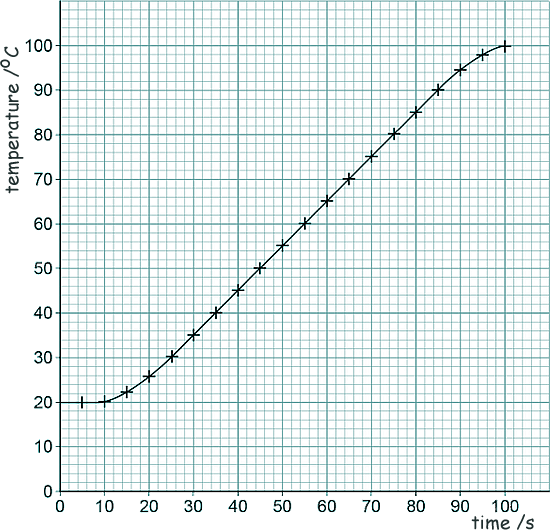
[1 mark] (c) Given that the resistance of the heating element in the kettle is 15 Ω and the current in the heating element is 12 A, calculate the power of the heating element. P = IV V = IR so, P = I2R P = 122 x 15 P = 144 x 15 P = 2160 W [3 marks] (d) Lily investigated how quickly the kettle could increase the temperature of 0.50 kg of water. Here is a graph of her results of the investigation:
The temperature of the water did not start to increase until 10 seconds after the kettle box was switched on. What is the reason for this? ( Tick one box).
[1 mark] (e) Describe a method Lily could have used to obtain the results shown in the graph.
- the examiner looks for relevant points - but also for a logical sequence... It is not just a 'tick fest' - but a marker does look to see how many relevant points you have made, then considers how you have strung them together to put your answer into a 'level'
Indicative content:
[6 marks] (f) The mass of water in the kettle was 500 g. The temperature of the water increased from 20 °C to 100 °C. Given that the specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg °C , calculate the energy transferred to the water. Δθ = 100 - 20 = 80 °C m = 500 g = 0.50 kg E = mcΔθ E = 0.50 × 4200 × 80 E = 168 000 J [4 marks] (g) The water in the kettle boiled for a short time before the kettle switched off. During this time 5.0 g of water changed to steam. Given that the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water = 2,260,000 J/kg, calculate the energy transferred to change the water to steam. m = 5.0 g = 0.005 kg E = mL E = 0.005 × 2,260,000 E = 11,300 J [3 marks] (20 marks total) |
Follow me...
|