GCSE Questions: Medical Physics
- scanning and therapy
Q7. X-rays and ultrasound can both be used for scanning internal organs.
(a) Ultrasound is used to scan unborn babies but X-rays are not used to scan unborn babies.
Explain why.
Ultrasound is non-ionising radiation  but X-rays are ionising radiation
but X-rays are ionising radiation  so X-rays increase the health risks (cancer, stunted growth, impaired brain function etc.) to the (unborn) baby.
so X-rays increase the health risks (cancer, stunted growth, impaired brain function etc.) to the (unborn) baby.
[3 marks]
(b) The behaviour of ultrasound waves when they meet a boundary between two different materials is used to produce an image.
Describe how.
Ultrasound/waves are partially reflected  when they meet a boundary between two different media/substances/tissues. The time taken for the pulse to travel to the boundary and back
when they meet a boundary between two different media/substances/tissues. The time taken for the pulse to travel to the boundary and back  to the probe is measured and is used to the determine distances travelled.
to the probe is measured and is used to the determine distances travelled.
[2 marks]
(c) The diagram below shows two pulses from a scan of an unborn baby.
The emitted pulse is labelled A.
The returning pulse picked up by the receiver is labelled B.
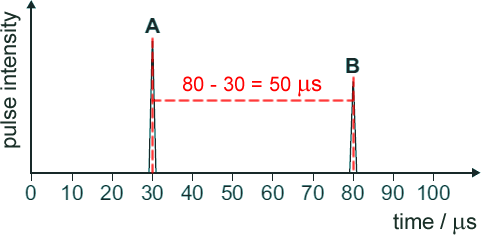
The closest distance between the unborn baby and the mother's skin is 4.0 cm.
Use information in the diagram above to calculate the average speed of the pulse.
Time between pulses = 50 =μs = 50 x 10-6 s 
Distance travelled = 8.0 cm = 8.0 x 10-2 m 
Speed = distance/time
Speed = 8.0 x 10-2/ 50 x 10-6
Speed = 1600 m/s 
[3 marks]
(Total 8 marks)


