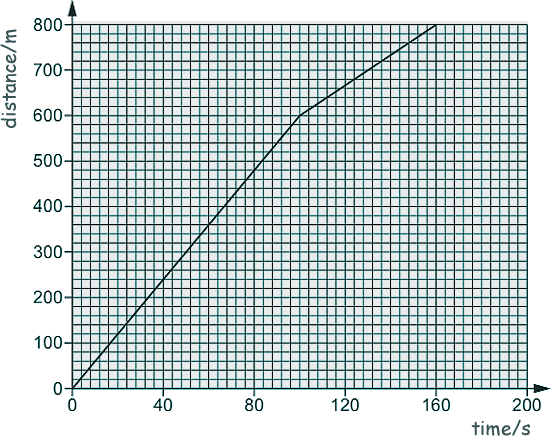
Multiple Choice: Forces, Dynamics and Mechanics Q11. Use a distance-time graph for a journey to school to calculate the average speed for the journey.
Q12. Which of the following is Newton's Third Law?
Q13. On Mars the gravitational field strength is 4.0 N/kg. How much would a 60 kg person weigh on Mars?
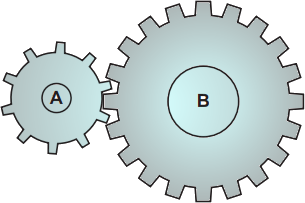
Q14. A student sets up two cogs. Cog A has 10 teeth and cog B has 20 teeth.
Cog A is turned two times. How many times does cog B turn?
Q15. A car travels at 72 km/h. How fast is this in metres per second (m/s)?
Q16. Which one of the following uses of forces causes a rotation?
Q17. A skydiver falls from a plane.
What is the name of the downward force in the diagram?
Q18. A cyclist travels 750 m in 50 seconds. Calculate the speed of the cyclist.
Q19. On the Moon the gravitational field strength is 1.6 N/kg. Calculate the weight of a 80 kg astronaut on the moon.
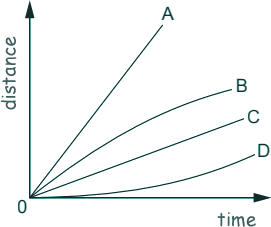
Q20. Look at the distance-time sketch graph below.
Which line shows the largest average speed?
|
Follow me...
|