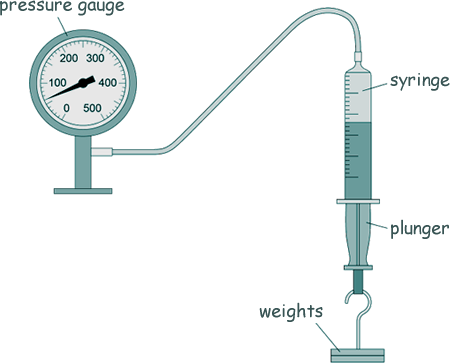
GCSE Questions: Kinetic Theory - Gases Q6. Professor Snape demonstrated the relationship between the pressure in a gas and the volume of the gas. The diagram below shows the equipment used.
This is the method used.
(a) What was the range of force used? 0.0 N - 12.0 N [1 mark] (b) Give one control variable in the investigation. Mass of gas (in the syringe) or temperature (of the gas) [1 mark] (c) When the volume of gas in the syringe was 45 cm3, the pressure gauge showed a value of 60 kPa. Calculate the pressure in the gas when the volume of gas in the syringe was 40 cm3. Give the answer to the correct number of significant figures for the data you have been given. P1V1 = P2V2= constant value P1 x 40 = 60 x 45 P1 = 60 x 45/40 P1 = 67.5 kPa
P1 = 68 kPa [5 marks] (d) When the volume of gas in the syringe increased, the pressure on the inside walls of the syringe decreased. Explain why. There is more time between collisions of particles and the walls of the syringe when the volume increases [3 marks] [10 Marks TOTAL] |
Follow me...
|