Questions on Heat Transfer
Q1.A cup should keep a hot beverage warm for as long as possible. The diagram shows three cups designed to take on a camping trip. All three cups are the same size and the same colour and finish.
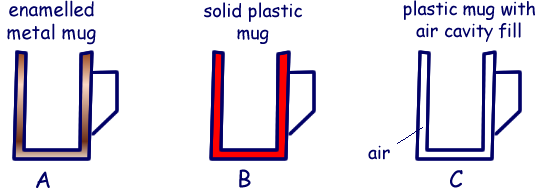
(i) Explain why when you hold a hot drink in cup A it is likely to cool down more quickly than a hot drink in cup B.
Both mugs will lose initially lose heat energy to the atmosphere from the space above the liquid at the same rate. It is the rate at which heat is lost through the body of the cup that will differ. 
Hotter surfaces transfer energy to the surroundings more quickly than cooler ones (see U-values).  Metals are good conductors of heat energy whereas plastics are insulators.
Metals are good conductors of heat energy whereas plastics are insulators.  Therefore the outer surface of cup A will get to the temperature of the hot drink very quickly, whereas the outer suface of cup B will be cooler for longer.
Therefore the outer surface of cup A will get to the temperature of the hot drink very quickly, whereas the outer suface of cup B will be cooler for longer.  Heat will therefore be radiated
Heat will therefore be radiated  to the surroundings much quicker from cup A, making the drink cool down more quickly.
to the surroundings much quicker from cup A, making the drink cool down more quickly.
(3 marks maximum)
(ii) Cup C is made from the same plastic as cup B. Explain why cup C is likely to keep the drink warmer for longer than cup B.
Air is a better insulator than plastic.  Therefore the air cavity will slow down the heat transfer rate to the outer surface of the cup.
Therefore the air cavity will slow down the heat transfer rate to the outer surface of the cup.  This will reduce the rate of heat transfer via radiation to the surroundings .
This will reduce the rate of heat transfer via radiation to the surroundings .
(2 marks maximum)
 (c) Walkers and campers are often advsed to take a 'survival blanket' with them. A survival blanket is made of a light, thin, shiny material.
(c) Walkers and campers are often advsed to take a 'survival blanket' with them. A survival blanket is made of a light, thin, shiny material.
Explain which feature of the blanket's design would enable a person to retain body heat.
Shiny sufaces are poor radiators of heat.  Therefore the shiny surface of the blanket
Therefore the shiny surface of the blanket  reduces the escape of body heat to the surroundings.
reduces the escape of body heat to the surroundings.
(2 marks)
Maximum 9 marks




 (c) Walkers and campers are often advsed to take a 'survival blanket' with them. A survival blanket is made of a light, thin, shiny material.
(c) Walkers and campers are often advsed to take a 'survival blanket' with them. A survival blanket is made of a light, thin, shiny material. 


