|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
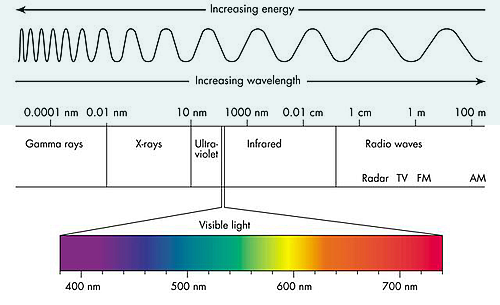
| Gamma
Rays |
Radioactive
nuclei |
Geiger-Müller
tube |
10-12 m |
 Radiotherapy Radiotherapy
 Diagnostic
work with a gamma
camera Diagnostic
work with a gamma
camera
 Pipe
leakage Pipe
leakage
|

cancer and mutations
deep in the body |
| X-Rays |
X-ray
tubes - produced when high energy electrons hit a metal target.
Also
given out from black holes and very bright stars |
Photographic
film |
10-10 m
(size
of an atom) |
|

cancer and mutations deep in the body
|
| Ultra
Violet (UV) |
Very hot objects, sun, sparks, mercury lamps. |
Photographic
film, skin (it causes sun tans and skin cancer -see ozone
layer depletion), makes fluorescent things glow with visible
light. |
10-8 m |
 Security
marking Security
marking
 Insect capture Insect capture
|

skin cancer and
cateracts |
| Visible Light |
Very hot objects - like the Sun or stars, hot metals (filament lamp), fluorescent objects, and visible lasers, LEDs. |
|
10-7 m
(Red
end is about 700nm
Blue end is about 400nm) |
 One
of our main forms of one to one communication! One
of our main forms of one to one communication!
 Warning
of dangers and location of food etc. Warning
of dangers and location of food etc.
 Writing,
painting etc. Writing,
painting etc.
|
Very bright
light can damage the retina
|
| Infra
Red (IR) |
Warm or Hot objects, sun, IR lasers |
Skin,
a blackened thermometer, a thermistor. |
10-5 m |
 To
keep us warm To
keep us warm
 To
cook food To
cook food
 Remote
control devices for TV etc. Remote
control devices for TV etc.
|
High intensity
can burn the skin and retina
|
Microwaves
Here is a link to news stories about possible dangers of microwave radiation
|
Short wave radio transmitters (cell (mobile) phone communications) and microwave
ovens (these contain a magnetron - a high-powered vacuum tube that generates coherent microwaves). |
Aerial
with a short wave radio set, or a satellite dish.
Water
filled objects (such as food) get very hot |
cm |
|
High intensity
and/or energy can cause heating effects within tissue - whether other
biological effects take place is debatable - some scientist think
it may cause tumour growth - but this is not by the route recognized
(it is none ionizing)
|
| Radio
and TV waves |
Radio and TV transmitters |
Aerial
with a TV set or a radio set.
(radio waves
CANNOT be heard!!!!!) |
km |
 Media communications Media communications
|
None known
unless intensity is abnormally high
|