Solutions: Radioactivity Questions
Q16.
(a) The lead nuclide  is unstable and decays in three stages through α and β emissions to a different lead nuclide
is unstable and decays in three stages through α and β emissions to a different lead nuclide  . The position of these lead nuclides on a grid of neutron number, N, against proton number, Z, is shown on the grid below:
. The position of these lead nuclides on a grid of neutron number, N, against proton number, Z, is shown on the grid below:
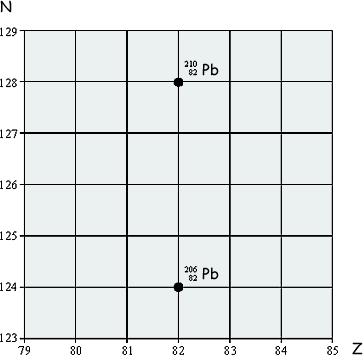
On the grid draw three arrows to represent one possible decay route.
Label each arrow with the decay taking place.
α decay will result in a diagonal line to the left - reducing both neutrons and proton by 2. One mark was awarded for a correctly drawn and labelled arrow for an alpha decay
β decay will result in a diagonal line to the right - reducing neutrons by 1 and incresing protons by 1. One mark was awarded for a correctly drawn and labelled arrow for a beta decay
The final mark was for putting in all three to get to the great granddaughter nuclide.  The examiner didn't might what order you put the decays in:
The examiner didn't might what order you put the decays in:
(3 marks)
(b) The copper nuclide 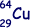 may decay by positron emission or by electron capture to form a nickel (chemical symbol - Ni) nuclide. Write the two equations that represent these two possible modes of decay.
may decay by positron emission or by electron capture to form a nickel (chemical symbol - Ni) nuclide. Write the two equations that represent these two possible modes of decay.
One mark for the correct symbol for the nickel nuclide - one mark for knowing there is an electron neutrino released in the reaction. Then one mark for each totally correct equation.
Positron Emission:
 →
→ 
 +
+ 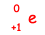 + νe
+ νe 

Electron Capture:
 +
+  →
→  + νe
+ νe 
(4 marks)
(c) The nucleus of an atom may be investigated by scattering experiments in which radiation or particles bombard the nucleus.
Name one type of radiation or particle that may be used in this investigation and describe the main physical principle of the scattering process.
State the information which can be obtained from the results of this scattering.
α particles  use coulomb/electrostatic/electromagnetic repulsion [or K.E. converted to P.E. (as α particle approaches nucleus)]
use coulomb/electrostatic/electromagnetic repulsion [or K.E. converted to P.E. (as α particle approaches nucleus)]  to obtain information about : proton number, nuclear charge, upper limit to nuclear radius or the fact that the mass of nucleus is most of the mass of atom
to obtain information about : proton number, nuclear charge, upper limit to nuclear radius or the fact that the mass of nucleus is most of the mass of atom 
(High energy) electron scattering  uses the diffraction of de Broglie Waves by nucleus
uses the diffraction of de Broglie Waves by nucleus  to obtain information on nuclear radius or nuclear density.
to obtain information on nuclear radius or nuclear density.
(3 marks)
(Total 10 marks)


