Solutions: Radioactivity Questions
Q14.
The diagram below shows a grid of neutron number against proton number. A nucleus  is marked in place:
is marked in place:
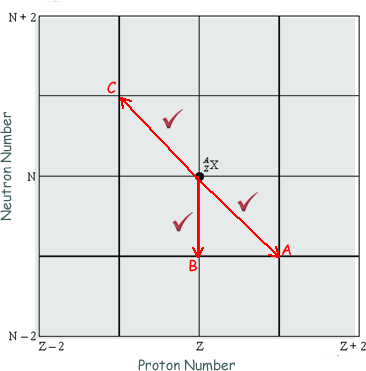
(a) Draw arrows on the grid, each starting on X and ending on a daughter nucleus after the following transitions:
(i) β– emission (label this arrow A), neutron emission (label this arrow B), electron capture (label this arrow C).
(ii) Give the equation for electron capture by the nucleus  .
.
 +
+ 
 +
+ 

(4 marks)
(b) When  decays to
decays to  by β– decay, the daughter nucleus is produced in one of two possible excited states. These two states are shown in below together with their corresponding energies.
by β– decay, the daughter nucleus is produced in one of two possible excited states. These two states are shown in below together with their corresponding energies.
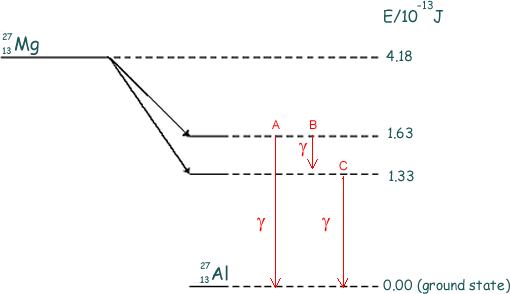
(i) Calculate the maximum possible kinetic energy, in J, which an emitted β– particle can have.
(ii) The excited aluminium nuclei emit γ-photons. Calculate each of the three possible γ-photon energies
1.63 x 10-13 J
1.33 x 10-13 J
(1.63 - 1.33) x 10-13 J = 0.30 x 10-13 J  (all three must be correct for the one mark)
(all three must be correct for the one mark)
(iii) Calculate the frequency of the most energetic photon emitted.
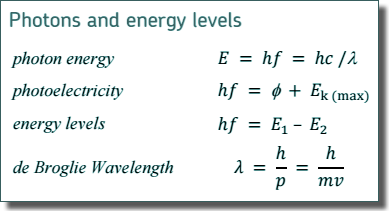
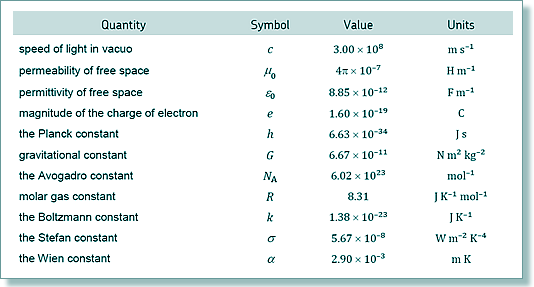
E = hf
f = E/h
f = 1.63 x 10-13/(6.63 x 10-34)
f = 2.46 × 1020 Hz 
(3 marks)
(c)
(i) State and explain two precautions that should be taken when working with a sample of  in a school laboratory.
in a school laboratory.
 Handle the sample with (long) (30 cm) tweezers because the radiation intensity decreases with distance (inverse square law of radiation).
Handle the sample with (long) (30 cm) tweezers because the radiation intensity decreases with distance (inverse square law of radiation).
 Store the sample in a lead box (immediately) when not in use to avoid unnecessary time of exposure to radiation
Store the sample in a lead box (immediately) when not in use to avoid unnecessary time of exposure to radiation 
(ii) Discuss which of the two types of radiation, β– or γ, emitted from a sample of  would be the more hazardous.
would be the more hazardous.
γ rays are more penetrating and are therefore more hazardous, as they are able to easily penetrate and ionise the internal organs of the body. 
OR
β– particles are not as penetrating as gamma, but can still penetrate into the body when the source is outside. They are more hazardous than gamma because they are more ionising and damage by them will be more concentrated within the body tissue; thereby increasing the possibility of tissue damage or mutated cells proliferating.
(3 marks)
(Total 10 marks)


