Questions on the Photoelectric Effect
Q10. Sodium metal has a work function of 2.28 eV. An atom of sodium has an ionisation energy of 5.15 eV.
(a)
(i) State what is meant by work function.
The work function is the minimum energy required by an electron  to escape from a (metal) surface
to escape from a (metal) surface 
[2 marks]
(ii) State what is meant by ionisation energy.
Ionisation energy is the minimum energy that an electron in its ground state  must absorb in order to be removed from the atom.
must absorb in order to be removed from the atom.
[2 marks]
(b) Show that the minimum frequency of electromagnetic radiation needed for a photon to ionise an atom of sodium is about 1.2 × 1015 Hz.
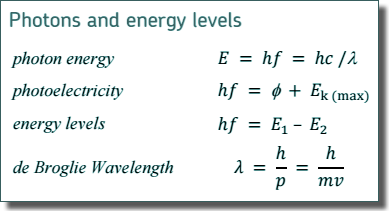
5.15 eV = 5.15 × 1.60 × 10-19J 
E = hf
5.15 × 1.60 × 10-19= 6.63 × 10-34 × f
f = 5.15 × 1.60 × 10-19/6.63 × 10-34 
f = 1.24 × 1015 Hz
[2 marks]
(c) Electromagnetic radiation with the frequency calculated in part (b) is incident on the surface of a piece of sodium.
Calculate the maximum possible kinetic energy (in joules) of an electron that is emitted when a photon of this radiation is incident on the surface.
Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
Φ = 2.28 × 1.60 × 10-19 = 3.65 × 10-19 J 
hf = Ek + Φ
Ek = 5.15 × 1.60 × 10-19 - 3.65 × 10-19= 4.59 × 10-19 J (
(  - for 3sf)
- for 3sf)
[3 marks]
(d) Calculate the speed of an electron that has the same de Broglie wavelength as the electromagnetic radiation in part (b).

c=fλ
λ = c/f = 3.0 x 108/1.24 × 1015
λ = 2.42 × 10-7m 
λdB = h/p = h/(mv)
v = h/mλdB = 6.63 × 10-34/(9.11 × 10-31 × 2.42 × 10-7 
v = 3010 m s-1
[3 marks]
(Total 12 marks)


