Momentum Questions - Solution
Q4. The diagram shows the velocity-time graph for a vertically bouncing ball, which is released above the ground at A and strikes the floor at B. The effects of air resistance have been neglected.
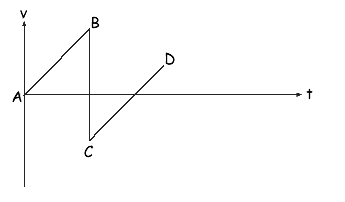
(a)
(i) What does the gradient of a velocity-time graph represent?
Acceleration
(ii) Explain why the gradient of the line CD is the same as line AB.
They both represent the acceleration of free fall [or the same acceleration]
(iii) What does the area between the line AB and the time axis represent?
The height/distance ball is dropped from above the ground [or the displacement of the ball from when it is dropped until it hits the ground]
(iv) State why the velocity at C is negative.
It is moving in the opposite direction to when it was at B
(v) State why the speed at C is less than the speed at B.
Some kinetic energy has been lost (or better still - transferred into heat energy) in the collision
[or it is an inelastic collision]
(5 marks)
(b) The ball has a mass of 0.15 kg and is dropped from an initial height of 1.2m. After impact the ball rebounds to a height of 0.75m.
Calculate
(i) the speed of the ball immediately before impact,
½ mv 2 = m gh so v 2 = 2 gh
v 2 = 2 × 9.81 × 1.2
v = 4.9 m s − 1 (4.85 m s − 1 )
(4.85 m s − 1 )
(ii) the speed of the ball immediately after impact,
½ mv 2 = m gh so v 2 = 2 gh
v 2 = 2 × 9.81 × 0.75
v = 3.8 m s − 1 (3.84 m s − 1 )
(3.84 m s − 1 )
(iii) the change in momentum of the ball as a result of the impact,
change in momentum = final momentum – initial momentum
= (0.15 × 3.84) − ( 0.15 × 4.85)
= − 1.3 kg m s − 1 (1.25 kg m s − 1 )
(1.25 kg m s − 1 )
(allow C.E. from (b)(i) and (b)(ii))
(iv) the magnitude of the resultant average force acting on the ball during impact if it is in contact with the floor for 0.10 s.
Ft =  p
p
F = D p/t = -1.3/0.10 = -13 N
(allow C.E. from (b)(iii))
(8 marks)
(Total 13 marks)
