Multiple choice questions should take you just under 2 minutes a question! Only one of the choices is correct. Q1. Which one of the following statements is correct?
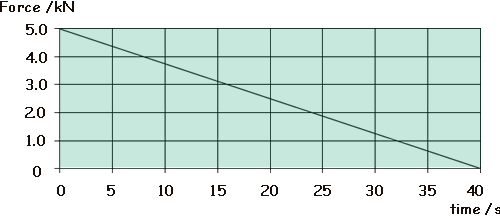
Ft = Q2. The graph shows how the force on a glider of mass 2000 kg changes with time as it is launched from a level track using a catapult.
Assuming the glider starts at rest what is its velocity in ms-1 after 40 s?
Area under graph is impulse so Ft = 0.5 x 5 x 40 = 100 kNs That is the change in momentum - initial momentum being zero we know that final momentum = 100 kNs mv = 100,000 N m = 2000 kg therefore v = 100,000/2000 = 50 m/s Q3. A gas molecule of mass m in a container moves with velocity v. If it makes an elastic collision at right angles to the walls of the container, what is the change in momentum of the molecule?
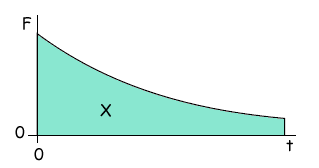
mv - (-mv) = 2mv Q4. The graph shows the variation with time, t, of the force, F, acting on a body.
What physical quantity does the area X represent?
Q5. Water of density 1000 kg m–3 flows out of a garden hose of cross-sectional area 7.2 × 10–4m2 at a rate of 2.0 × 10–4m3 per second. How much momentum is carried by the water leaving the hose per second?
density = mass/volume therefore mass = density x volume. You can then work out the mass delivered every second. That water is delivered like a 'tube' - you are given the CSA so you can work out the length of that tube. That length is the distance the water travels in a second - the velocity! Momentum = mv so the answer is (density x volume) x (volume / csa) Q6. Which row, A to D, in the table correctly shows the quantities conserved in an inelastic
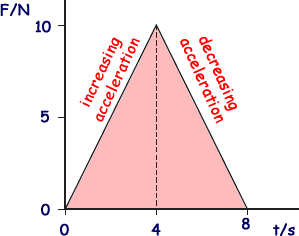
Inelastic collision - KE not conserved - a realy quick one to answer! Q7. A ball of mass 2.0 kg, initially at rest, is acted on by a force F which varies with time t as shown by the graph. What is the velocity of the ball after 8.0 s?
Impulse = area under graph = 40 Ns The impulse produces the change in momemtum, which, as the initial velocity was zero, will be equal to the final momemtum after 8 seconds. Final mv = 40 but m = 2.0 kg so v = 20 m/s
Q8. A body X moving with a velocity v makes an elastic collision with a stationary body Y of equal mass on a smooth horizontal surface.
Which line, A to D, in the table gives the velocities of the two bodies after the collision?
Elastic collision - therefore no loss of KE. Initial KE = ½mv2 but if velocities halve total KE will be halved therefore A and B cannot happen. The ball cannot continue at velocity v without pushing the other ball too - therefore C is wrong. Answer must be D |
Follow me...
|