A level: Ultrasound Questions
Q5.
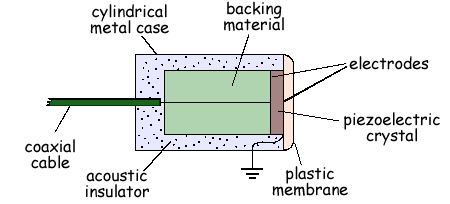
(a) Describe how pulses of ultrasound are produced by the transducer.
Electrodes are connected across an alternating, high frequency EMF(voltage/pd) source. The crystal expands and contracts at frequency of emf
The crystal expands and contracts at frequency of emf  [or resonates at same frequency]. The vibration of faces produces ultrasound/pressure waves.
[or resonates at same frequency]. The vibration of faces produces ultrasound/pressure waves.  A backing material damps the oscillations of crystal.
A backing material damps the oscillations of crystal.  to stop the crystal oscillating between end of transmitted pulse and start of reflective pulse
to stop the crystal oscillating between end of transmitted pulse and start of reflective pulse 
3 marks
(b) In an ultrasound A scan
(i) explain how the received signals are detected,
The probe acts as receiver and thereceived signal causes crystal to vibrate.  The vibration of crystal produces and alternating pd
The vibration of crystal produces and alternating pd 
(ii) state why it is essential to use short pulses of ultrasound.
The transmission must be completed before the reflected pulse can be recieved. 
3 marks
Total 6 marks


