Capacitor Questions
Q9. A sinusoidal alternating voltage supply is connected to a bridge rectifier consisting of four ideal diodes. The output of the rectifier is connected to a resistor R and a capacitor C as shown in the diagram.

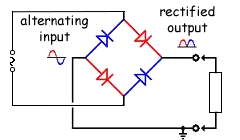
The function of C is to provide some smoothing to the potential difference across R.
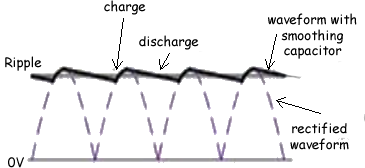
The variation with time t of the potential difference V across the resistor R is shown in the graph below.

(a) Use the graph to determine, for the alternating supply,
(i) the peak voltage
V0 = 4 volts 
(1 mark)
(ii) the root-mean-square (r.m.s.) voltage
VRMS= V0 / √2
VRMS= 2.8 volts 
(1 mark)
(iii) the frequency
Tsupply = 22 - 2 (see graph) = 20 ms 
f = 1/(20 x 10-3)
f = 50 Hz 
(2 marks)
(b) The capacitor C has capacitance 5.0 μF. For a single discharge of the capacitor through the resistor R, use the graph to
(i) determine the change in potential difference
ΔV = 4.0 - 2.4 (see graph) = 1.6V 
(1 mark)
(ii) determine the change in charge on each plate of the capacitor,
ΔQ = CΔV
ΔQ = 5.0 x 10-6 x 1.6
ΔQ = 8.0 x 10-6 C 
(2 marks)
(iii) show that the average current in the resistor is 1.1 × 10–3 A.
I = ΔQ /t
t = 7.0 x 10-3s (see graph) 
I = (8.0 x 10-6)/(7.0 x 10-3) 
I = 1.1 × 10–3 A Q.E.D.
(2 marks)
(c) Use the graph and the value of the current given in (b)(iii) to estimate the resistance of resistor R.
Average current = 1.1 × 10–3 A
(from the graph - midpoint between 4.0 and 2.4 = 2.4 + 1.6/2 = 2.4 + 0.8 = 3.2)
Average voltage = 3.2V 
V = IR
R = V/I = 3.2/ 1.1 × 10–3
R = 2900 Ω 
(2 marks)
(Total 11 marks)










