Nuclear Radius
Q7.
(a) Scattering experiments are used to investigate the nuclei of gold atoms.
In one experiment, alpha particles, all of the same energy (monoenergetic), are incident on a foil made from a single isotope of gold.
(i) State the main interaction when an alpha particle is scattered by a gold nucleus.
The electromagnetic (or electrostatic or Coulomb) interaction 
[1 mark]
(ii) The gold foil is replaced with another foil of the same size made from a mixture of isotopes of gold. Nothing else in the experiment is changed.
Explain whether or not the scattering distribution of the monoenergetic alpha particles remains the same.
The scattering distribution remains the same because the alpha particles interact with a nucleus whose charge/proton number/atomic number remains the same and therefore the repulsive force remains the same.
The scattering distribution will change - it will become less distinct because there is a mixture of nuclear masses (which gives a mixture of nuclear recoils). 
[1 mark]
(b) Data from alpha-particle scattering experiments using elements other than gold allow scientists to relate the radius R, of a nucleus, to its nucleon number, A.
The graph below shows the relationship from the data obtained from a scattering experiment. The data obtained obeys the relationship R = r0 A1/3
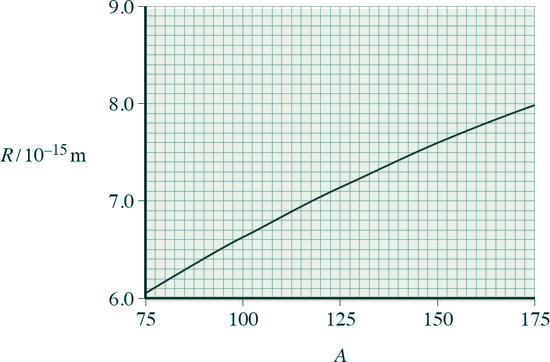
(i) Use information from the graph to show that r0 is about 1.4 × 10–15 m.
r0 = 8.0 x 10-15 / 1751/3
r0 = 1.43 x 10-15 m
[1 mark]
(ii) Show that the radius of a  nucleus is about 5 × 10–15 m.
nucleus is about 5 × 10–15 m.
R = r0 A1/3
R = 1.43 x 10-15 x 511/3
R = 5.3 x 10-15 m 
(R = 5.2 x 10-15 m from r0 = 1.4 x 10-15 m)
[2 marks]
(c) Calculate the density of a  nucleus. State an appropriate unit for your answer.
nucleus. State an appropriate unit for your answer.

density = mass / volume
m = (23 x 1.673 + 28 x 1.675) x 10-27
m = 8.5 x 10-26 kg
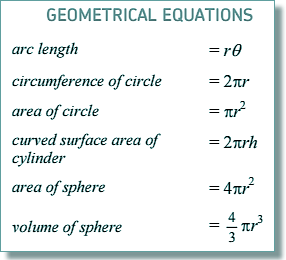
V = 4/3 π
r3
V = 4/3 π
(5.3 x 10
-15
)3
V = 6.24 x 10-43 m3
 ρ
= m/V
ρ
= m/V
ρ
= 8.5 x 10-26/6.24 x 10-43 = 1.37 x 10 17
= 1.37 x 10 17
ρ
= 1.4 x 10
17 kg m-3
kg m-3
[3 marks]
(Total 8 marks)


