GCSE Level Questions: Transformers
Q2.
(a) The basic structure of a transformer is a primary coil of insulated wire, an iron core and a secondary coil of insulated wire.
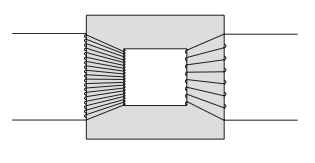
(i) Why is the core made of iron?
Iron is a soft magnetic material  so it (quickly) becomes magnetised when placed in a magnetic field and (quickly) loses its magnetism when the field is removed
so it (quickly) becomes magnetised when placed in a magnetic field and (quickly) loses its magnetism when the field is removed 
Any reference to conduction of electricity/heat nullifies the mark
(Max 1 mark)
(ii) Explain how a transformer works.
any four from:
 insulation prevents electricity/current flowing through the iron/core
insulation prevents electricity/current flowing through the iron/core 
 alternating current/a.c. in the primary (coil)
alternating current/a.c. in the primary (coil) 
 produces a changing magnetic field (in the iron/core)
produces a changing magnetic field (in the iron/core) 
 and hence the secondary (coil) experiences this changing magnetic field
and hence the secondary (coil) experiences this changing magnetic field 
 inducing an alternating potential difference/p.d./voltage across the secondary (coil)
inducing an alternating potential difference/p.d./voltage across the secondary (coil) 
 (this results in) alternating current/a.c. in the secondary (coil)
(this results in) alternating current/a.c. in the secondary (coil) 
(4 marks)
(b) A small step-down transformer is used in the charger for an electric screwdriver. The input to the transformer is 230 V a.c. mains supply and the output is 5.75 V a.c. There are 3200 turns on the primary coil.

Calculate the number of turns on the transformer's secondary coil.
Show clearly how you work out your answer
Ns = VsNp/Vp
= 5.75 x 3200/230 
= 80
number of turns number of turns on secondary = 80 
(2 marks)
(Total 7 marks)


