GCSE level optics questions
Q2.
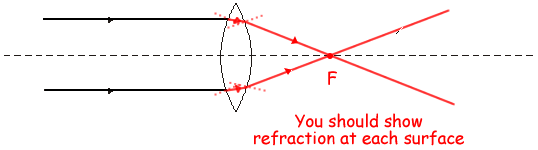
(a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis.
(i) Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays.
If diagram brings the rays to a point on the axis award 1 mark.
If the diagram shows refraction at each boundary award 2 marks. 

(2 marks)
(ii) Name the point where the rays come together.
The principal focus OR focal point. 
(1 mark)
(iii) What word can be used to describe this type of lens?
Convex lens or converging lens. 
(1 mark)
(b) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis.

(i) Which point A, B, C, D or E shows the focal point for this diagram?
A 
(1 mark)
(ii) Explain your answer to part (b)(i).
The focal point must be A as this is a diverging (or concave) lens. The rays are seen to diverge from the virtual focus. 
(1 mark)
(iii) What word can be used to describe this type of lens?
Convex lens or diverging lens. 
(1 mark)
(c) Complete the following three sentences by choosing the correct words from each bracketed section.
In a camera a converging lens is used to produce an image on a (film/lens/screen) 
The image is (larger than/smaller than/the same size as) the object. 
Compared to the distance of the image from the lens, the object is (further away from/nearer to/the same distance from) the lens. 
(3 marks)
(d) Explain the difference between a real image and a virtual image.
A real image of a point on an object is formed where rays of light converge at a point.  If a screen is placed at that point the image will appear on the screen.
If a screen is placed at that point the image will appear on the screen.  A virtual image is formed only by the eye of the beholder. The rays from which the image is formed are diverging, they never meet at a point, therefore they cannot form an image that is picked up on a screen.
A virtual image is formed only by the eye of the beholder. The rays from which the image is formed are diverging, they never meet at a point, therefore they cannot form an image that is picked up on a screen. The brain/eye of the beholder traces back the light rays entering the ye and perceives an image at the point they trace back to.
The brain/eye of the beholder traces back the light rays entering the ye and perceives an image at the point they trace back to.  (Max 3)
(Max 3)
(3 marks)
(Total 13 marks)


