Heat Questions - GCSE Level
Q9. The diagram shows a drink chiller in use. The cold drink chiller is inserted into a warm bottle of drink, so the temperature of the drink decreases.
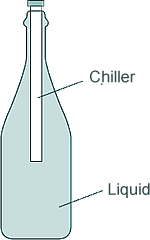
(a) Explain how a convection current is formed in the drink in the bottle.
The liquid molecules or particles next to the chiller become cooler - the liquid therefore contracts as the particles move closer together
- the liquid therefore contracts as the particles move closer together . This means the liquid near to the chiller becomes more dense than the surrounding warmer liquid and sinks
. This means the liquid near to the chiller becomes more dense than the surrounding warmer liquid and sinks . Warmer, less dense, liquid rises
. Warmer, less dense, liquid rises to replace the dener, warmer liquid.
to replace the dener, warmer liquid.
[4 marks]
(b) As the chiller warms, the drink cools. State how the rate of energy transfer from the drink to the chiller changes as the chiller warms. Give a reason for your answer.
The rate of energy transfer decreases  as the temperature difference
as the temperature difference  between chiller and liquid decreases.
between chiller and liquid decreases.
[2 marks]
(c) As the drink bottle cools down, water vapour in the air condenses on the outside of the bottle. Explain why.
The bottle cools the air around it as the air transfers energy to the bottle.  In the cooler air the
water molecules / particles move closer together
In the cooler air the
water molecules / particles move closer together  and condense to form droplets of liquid
and condense to form droplets of liquid on the cool bottle surface.
on the cool bottle surface.
[3 marks]
(9 marks total)







