Energy Transfer Questions - GCSE Level
Q2.
(a) In winter, energy is transferred from the warm air inside a house to the air outside.
(i) What effect will the energy transferred from the house have on the air outside? (1 mark)
It will make it warmer or it raises the temperature of the air.
Accept it produces a convection (current) or it makes it less dense.
(ii) What would happen to the energy transfer if the temperature inside the house
were reduced? Assume the temperature outside the house does not change.
(1 mark)
It reduces or slows down 
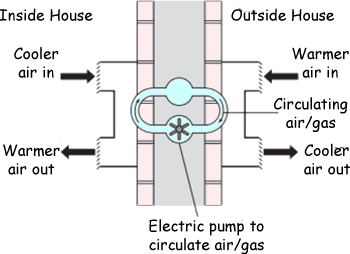
(b) To increase energy efficiency, a householder installs a heat exchanger to an outside wall of the house. The heat exchanger uses heat from the air outside to warm the inside of the house. The diagram shows the idea of the heat exchanger.
(i) Why does the heat exchanger cost money to run? (1 mark)
Electricity for the electrical energy (to run the pump) must be paid for. 
(ii) The heat exchanger is cost effective in reducing energy consumption. Explain why. (2 marks)
For two marks:

More useful (heat) energy is transferred into the house than the energy used to operate the pump
OR
Reduced cost of heating the house is greater than the cost of running the (electrical) pump.
OR
It costs little to run compared to the savings made
For one mark:
- reduces energy bills or reduced fuel costs / heating costs
No mark for simply putting 'It is cheap'.
(5 marks total)


