GCSE Questions - Electromagnetic Spectrum
Q3.
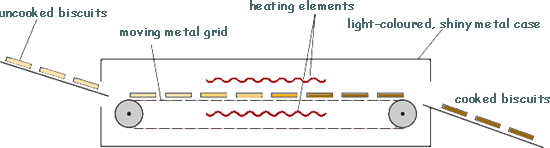
The diagram above shows a way that biscuit manufacturers can cook large quantities of biscuits.
The uncooked biscuits are placed on a moving metal grid. The biscuits pass between two hot electrical heating elements inside an oven. The biscuits turn brown as they cook.
The oven has two control knobs, as shown in in the diagram below.

(a) Which type of electromagnetic radiation makes the biscuits turn brown? [1 mark]
infra-red radiation 
(b) Suggest two ways of cooking the biscuits in this oven, to make them turn browner.
pass the biscuits through a second time.  [2 marks maximum]
[2 marks maximum]
(c) The inside and outside surfaces of the oven are light-coloured and shiny. Explain why.
Infra-red radiation is reflected by shiny surfaces.  The radiation given off from the heating elements would therefore be reflected back from the inside of the oven towards the bicuits, increasing the efficiency of the oven.
The radiation given off from the heating elements would therefore be reflected back from the inside of the oven towards the bicuits, increasing the efficiency of the oven. The outside surface being shiny reduces the loss of energy from the oven, as shiny surfaces are poor emitters of radiation.
The outside surface being shiny reduces the loss of energy from the oven, as shiny surfaces are poor emitters of radiation.
[3 marks maximum]
(Total 6 marks)


