Questions on Electric Circuits
Q13.
A circuit is shown below.
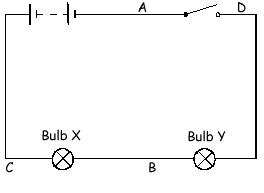
(a) The switch is open. Steven connects point A to point B with a piece of copper wire. Which bulbs, if any, light up?
Bulb X 
1 mark
(b) Steven removes the copper wire and uses it to connect point C to point D. The switch is still open. Which bulbs, if any, light up?
Neither light up. 
1 mark
(c) Steven removes the copper wire and closes the switch. Both bulbs light up, but not very brightly. He then uses the copper wire to connect point B to point C.

(i) What happens to bulb X?
It goes out 
1 mark
(ii) What happens to bulb Y?
It gets brighter. 
1 mark
(d) Steven removes the copper wire. The switch is still closed. Both bulbs light up, but not very brightly. He then uses the copper wire to connect point A to point B.

(i) What happens to bulb X?
It gets brighter.
1 mark
(ii) What happens to bulb Y?
It goes out. 
1 mark
Maximum 6 marks


