|
Click here to download a worksheet on this topic.
This
is a very important physics discovery...
Our modern lifestyle would not
be possible without electric power generation.... and electromagnetic
induction is the process by which wind, wave, tidal, HEP, oil, gas, coal,
nuclear and biomass energy is changed into electricity.
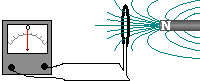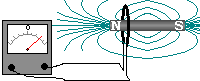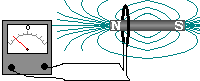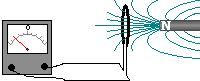 If a magnet is moved into a coil
of wire which is part of a complete circuit a voltage is induced across
the ends of the wire - a current is produced (induced) in the wire. If a magnet is moved into a coil
of wire which is part of a complete circuit a voltage is induced across
the ends of the wire - a current is produced (induced) in the wire.
If
the magnet is then moved out of the coil, or the other pole of the magnet
is moved into the coil, the direction of the induced voltage (current)
is reversed.
Click
here
for an interactive demonstration.
Size of the current produced
The
size of the induced voltage depends upon the 'rate of cutting of magnetic
flux lines'
So:
 If
the magnet is stationary with respect to the magnetic field
no voltage is induced and therefore no current flows. If the wire
'cuts through' the lines of magnetic flux (crosses through field lines)
a current is registered on a sensitive galvanometer (either a voltmeter
or ammeter). If
the magnet is stationary with respect to the magnetic field
no voltage is induced and therefore no current flows. If the wire
'cuts through' the lines of magnetic flux (crosses through field lines)
a current is registered on a sensitive galvanometer (either a voltmeter
or ammeter).
 The faster the magnet 'cuts the magnetic flux lines' the bigger
the voltage and the bigger the current flow. As if you move the
magnet faster you cut through more lines of magnetic magnetic flux
in a given time and you therefore get a bigger induced current and
voltage. The faster the magnet 'cuts the magnetic flux lines' the bigger
the voltage and the bigger the current flow. As if you move the
magnet faster you cut through more lines of magnetic magnetic flux
in a given time and you therefore get a bigger induced current and
voltage.
 The
more turns of the wire that 'cut the magnetic flux lines'
(possible if you wind the wire into a coil!) the bigger the voltage
and current induced. The
more turns of the wire that 'cut the magnetic flux lines'
(possible if you wind the wire into a coil!) the bigger the voltage
and current induced.
 If
you use a stronger magnet the magnetic flux lines are closer
together - therefore as you move the magnet it cuts through more
lines in a given time and you get a bigger induced current and voltage. If
you use a stronger magnet the magnetic flux lines are closer
together - therefore as you move the magnet it cuts through more
lines in a given time and you get a bigger induced current and voltage.
 If the coil face
has a bigger area the total flux intercepted by it will be
bigger If the coil face
has a bigger area the total flux intercepted by it will be
bigger
The direction of the current produced
The direction of the induced current flow can be worked out using Fleming's Right Hand Rule.
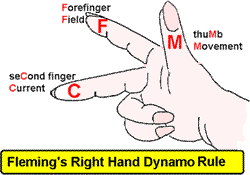 Your thumb and first two fingers are held mutually at right angles as shown in the diagram. Your thumb and first two fingers are held mutually at right angles as shown in the diagram.
 Your thuMb represents the direction of the Movement of the wire in the magnetic field. Your thuMb represents the direction of the Movement of the wire in the magnetic field.
 Your Forefinger represents the direction of the magnetic Field Your Forefinger represents the direction of the magnetic Field
 Your seCond finger represents the direction of the conventional Your seCond finger represents the direction of the conventional
Current flow.
 See here for a page of questions to test your understanding of this. See here for a page of questions to test your understanding of this.
Practical Application:
 The 'shake-to-charge' flashlight The 'shake-to-charge' flashlight
Also see:
 Lenz's Law Lenz's Law
 The Electric Generator The Electric Generator
 Transformers Transformers
|







 If a magnet is moved into a coil
of wire which is part of a complete circuit a voltage is induced across
the ends of the wire - a current is produced (induced) in the wire.
If a magnet is moved into a coil
of wire which is part of a complete circuit a voltage is induced across
the ends of the wire - a current is produced (induced) in the wire. Your thumb and first two fingers are held mutually at right angles as shown in the diagram.
Your thumb and first two fingers are held mutually at right angles as shown in the diagram.
