 pV=constant pV=constant
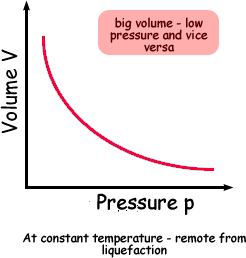
Boyle's Law describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature . The pressure is caused by the gas molecules bumping into the walls of the container.
The pressure exerted by a gas at constant temperature varies inversely with the volume of the gas. This means that if you increase the one the other must decrease so that when you multiply them together you get the same answer. For example, if the volume is halved, the pressure is doubled; and if the volume is doubled, the pressure is halved. |
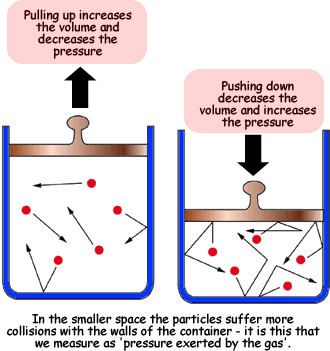 The reason for this effect is that a gas is made up of loosely spaced molecules moving at random. If a gas is compressed in a container, these molecules are pushed together; so, the gas occupies less volume. The molecules, having less space across which to move, hit the walls of the container more frequently and therefore exert an increased pressure. The reason for this effect is that a gas is made up of loosely spaced molecules moving at random. If a gas is compressed in a container, these molecules are pushed together; so, the gas occupies less volume. The molecules, having less space across which to move, hit the walls of the container more frequently and therefore exert an increased pressure.
Boyle's Law actually applies only to an ideal, theoretical gas. When real gases are compressed at a constant temperature, changes in the relationship between pressure and volume occur accoring to the law as long as the volume does not get too small (or the pressure too high). When that happens the gas starts to liquefy and a 'gas law' no longer applies!
The law is accurate enough to be useful in a number of practical applications. It is used, for example, in calculating the volume and pressure of internal-combustion engines and steam engines.
The law was first proposed in 1662 by Robert Boyle. In 1676, Edme Mariotte of France independently came to the same conclusion, and it is sometimes called Mariotte's Law.
Because pV = constant that means that p1V1 = constant and so does p2V2.
We can therefore write:
p1V1=p2V2 (at constant temperature)
where
 V1 equals the original volume, V1 equals the original volume,
 V2 equals the new volume, V2 equals the new volume,
 p1 equals the original pressure, p1 equals the original pressure,
 p2 equals the new pressure, p2 equals the new pressure,
To get a straight line graph you need to rearrange the equation into the form Y = mx+c
pV = constant
so, p = constant x 1/V
or, V = constant x 1/p
There is no intercept - the line goes through the origin. You have to think carefully about the units on the axes though.
What is the unit for pressure?
It is the pascal.... so what is the unit of the inverse of pressure?.... the inverse of the pascal... Pa-1
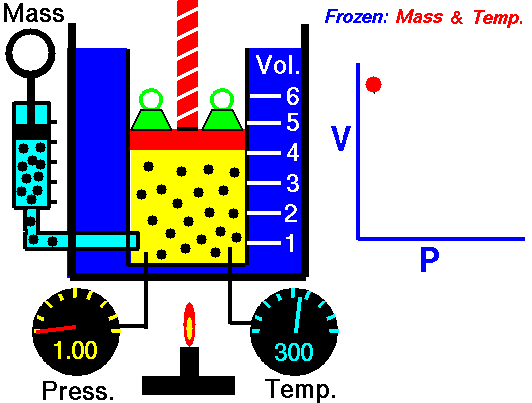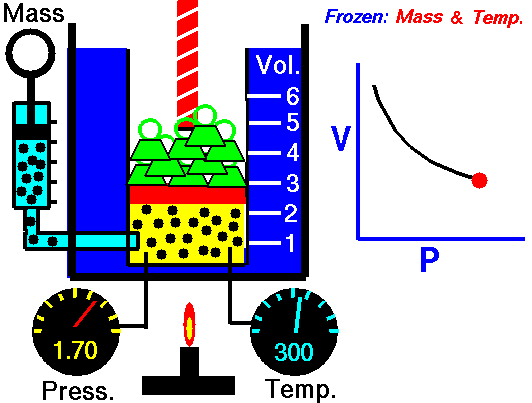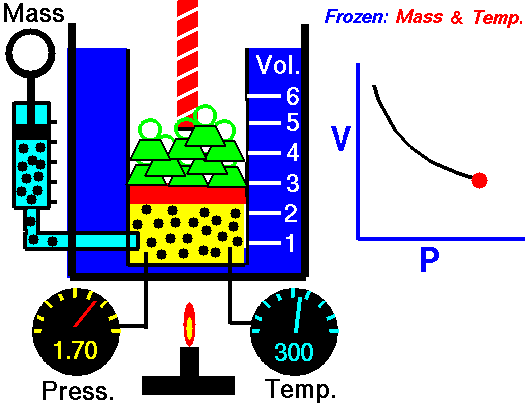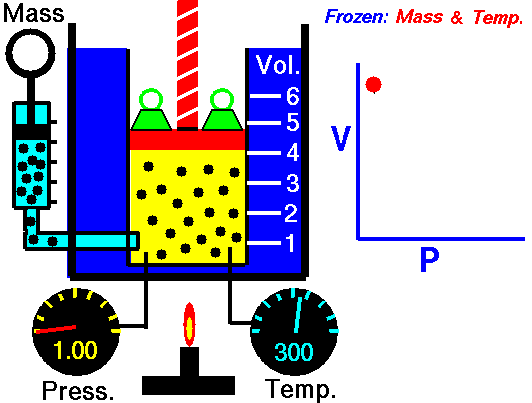
The above image is from the NASA site
|







 pV=constant
pV=constant


