|
||||

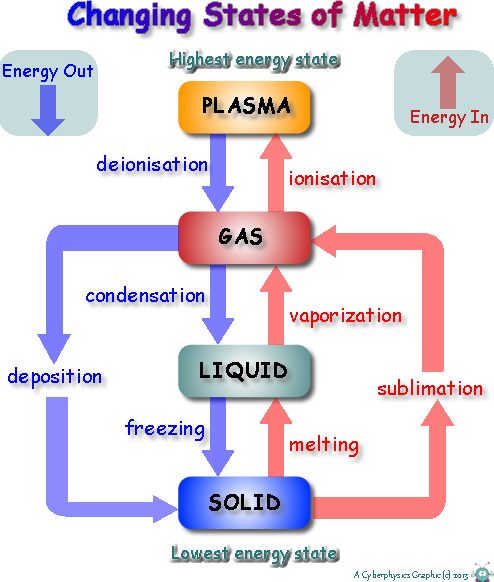
Changing State |
||||
|
We have seen that we can think of everything as being made up of particles, and that how these particles behave can be used to explain the differences between each of the three states of matter that we study at GCSE Level. In order to 'change state' energy is either 'taken in' or 'given out'.
When energy is taken in to change state it is used to 'free' particles from their neighbouring particles. It increases their internal potential energy. It does not increase kinetic energy... therefore does not cause a rise in temperature.
We think of 'changing state' as only occurring at boiling point and melting point temperatures, but that is not the case.
|
||||
 |
||||