    |
||||
 Volume
(V) Volume
(V) |
||||
|
'Volume' is the three dimensional space that an object occupies. You will have come across this idea at Primary School - and in your Mathematics lessons. In Physics you are expected to know how to find the volume of some common shapes. You will be expected to remember how to find the volume of the easy ones:
Other formulae will be given you to work from in the examination:
UNITSThe unit of volume is the cube of whatever unit of length used in the calculation. The SI unit of length is the metre so the SI unit of volume is the metre cubed (m3). Many calculations that you will be given up to GCSE level will involve centimetre cubed and millimetre cubed. Unless you are told otherwise do not attempt to change them into SI units.... if you do so and make a mistake you will lose marks. If you have to make a conversion, don't simply memorise the relationship work it out as below:
The calculation of a number for a volume is meaningless without the unit. The unit of the volume makes all the difference - a 1m3 tank holds a ton of water.... a 1 cm3 container only holds 1g of water.... a big difference!
L O Jones October 2001 |
||||
 |
||||

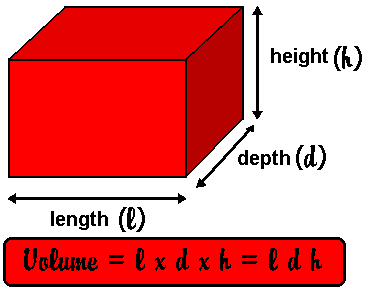
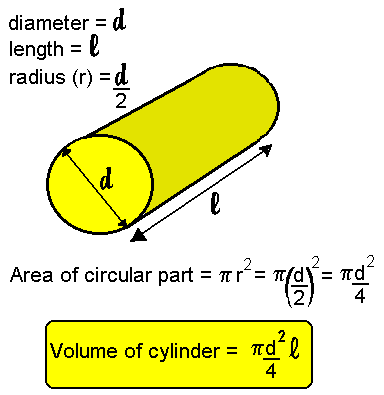
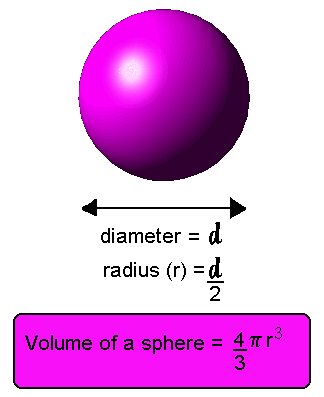

 For practical measurement of liquid volume see the page
on the use of a
For practical measurement of liquid volume see the page
on the use of a 
