A level: Radioactivity Questions
Q12. The isotope of uranium,  , decays into a stable isotope of lead,
, decays into a stable isotope of lead,  by means of a series of α and β– decays.
by means of a series of α and β– decays.
(a) In this series of decays, α decay occurs 8 times and β– decay occurs n times. Calculate n.
(1 mark)
(b)
(i) Explain what is meant by the binding energy of a nucleus.
(2 marks)
(ii) The graph belowshows the binding energy per nucleon for some stable nuclides.
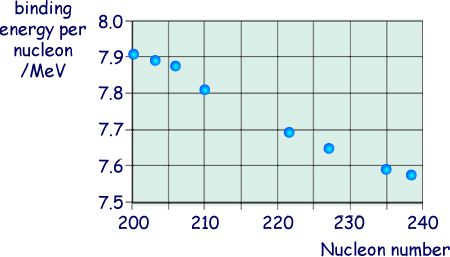
Estimate the binding energy, in MeV, of the  nucleus.
nucleus.
(1 mark)
(c) The half-life of  is 4.5 × 109 years, which is much larger than all the other half-lives of the decays in the series. A rock sample when formed originally contained 3.0 × 1022 atoms of
is 4.5 × 109 years, which is much larger than all the other half-lives of the decays in the series. A rock sample when formed originally contained 3.0 × 1022 atoms of  and no
and no  atoms.
atoms.
At any given time most of the atoms are either  or
or  with a negligible number of atoms in other forms in the decay series.
with a negligible number of atoms in other forms in the decay series.
(i) Using the axes below, sketch graphs to show how the number of  atoms and the number of
atoms and the number of  atoms in the rock sample vary over a period of 1.0 × 1010 years from its formation.
atoms in the rock sample vary over a period of 1.0 × 1010 years from its formation.
Label your graphs U and Pb.
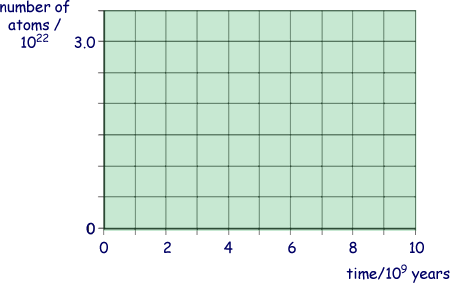
(2 marks)
(ii) A certain time, t, after its formation the sample contained twice as many  atoms as
atoms as  atoms.
atoms.
Show that the number of  atoms in the rock sample at time t was 2.0 × 1022.
atoms in the rock sample at time t was 2.0 × 1022.
(1 mark)
(iii) Calculate t in years.
(3 marks)
(Total 10 marks)



